I. Background Overview
In April 2025, the U.S. government initiated a new round of trade protection policies, imposing a 10% general tariff on almost all imported goods, and an additional "reciprocal tariff" on countries with significant trade surpluses. Among them, Vietnam faced an additional 46%, Cambodia 49%, Thailand 36%, and Indonesia 32%. Concurrently, as early as July of last year, the U.S. launched an anti-dumping investigation into large top-freezer refrigerators exported from Thailand, preliminarily determining a dumping margin as high as 165.47%. This series of policies has dealt a heavy blow to the exports of Southeast Asian countries, especially impacting downstream industries centered around polyurethane materials, such as refrigerators, soft furniture, and footwear.
II. Main Impacts on Southeast Asian Countries
1.Vietnam
Export Pressure Surge: The tariff soared to 46%, severely affecting Vietnam's exports to the U.S., particularly furniture and footwear.
Footwear Impact: As one of the world's largest athletic shoe producers, high tariffs will directly impact brand contract manufacturers including Nike and Adidas.

Soft Furniture Hit: The U.S. is Vietnam's largest furniture export market; increased tariffs will lead to a decrease in purchase orders, and a corresponding decline in the demand for polyurethane flexible foam.
2. Thailand
Economic Growth Slowdown: Tariff policies could slow down Thailand's GDP growth by 1 percentage point, prompting the government to consider fiscal stimulus.
Refrigerator Exports Hindered: The U.S. imposes a 165.47% anti-dumping duty on Thai refrigerators, nearly halting exports, significantly reducing consumption of polyurethane insulation materials.
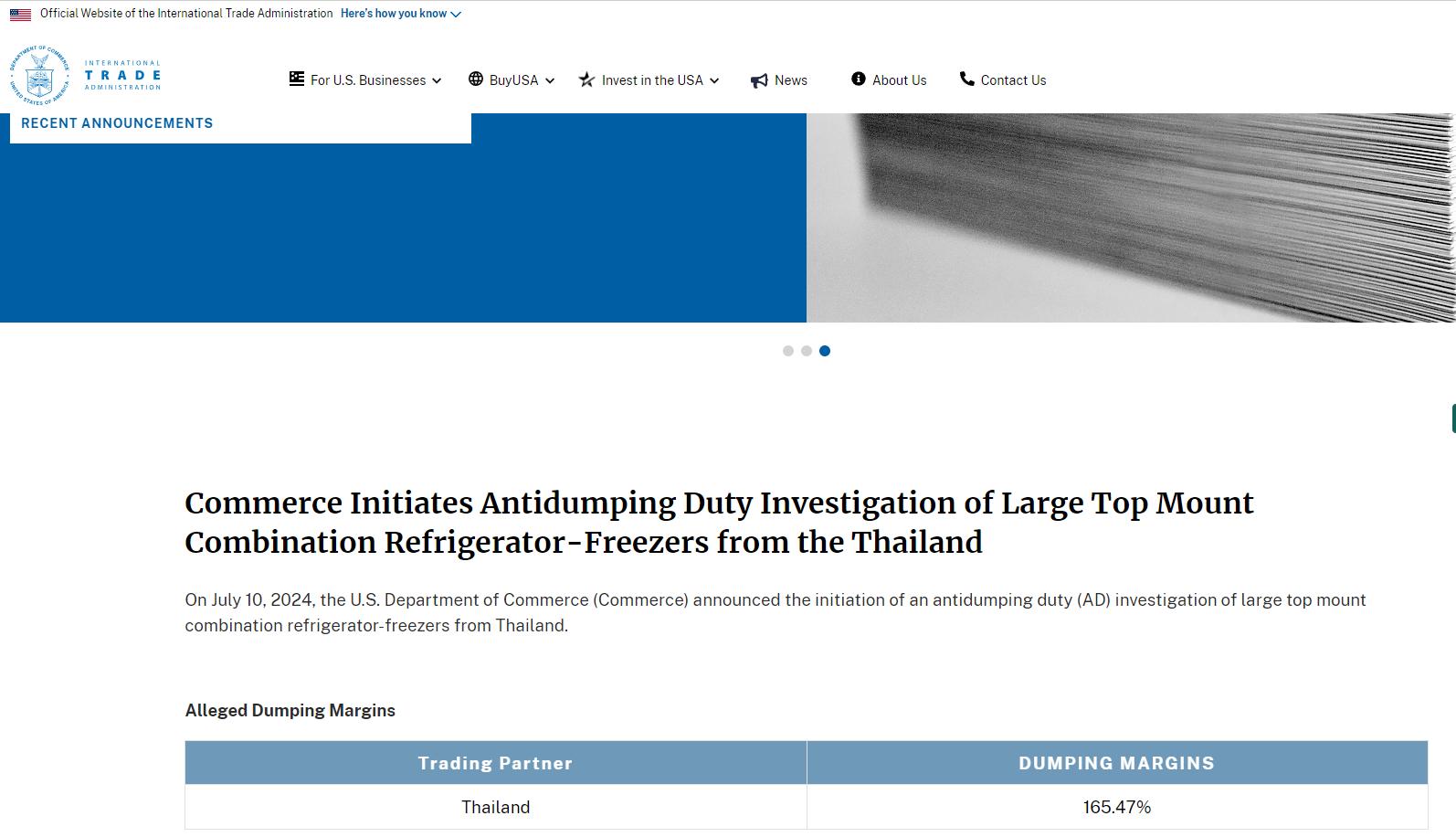
Source: U.S. Department of Commerce - Bureau of International Trade Administration
Polyurethane Industry Chain Reaction: From raw material suppliers to refrigerator manufacturers, companies face dual pressures of rising inventory and deteriorating profitability.
3. Indonesia
Footwear Hit: As one of the world's important footwear exporters, high tariffs significantly compress export profits for Indonesian footwear companies, potentially leading orders to flow to untaxed countries.
Furniture Industry Ripple Effect: With a high proportion of polyurethane foam used in furniture, a weak U.S. market will compress related deman
4. Cambodia and Malaysia
Cambodia: Export structure dominated by footwear and textiles will be greatly affected, with a significant decline in polyurethane footwear material demand.
Malaysia: Although not yet subject to high reciprocal tariffs, the 10% general tariff increases export burden, reducing competitiveness in industries such as refrigerators and furniture.
III. Impact Analysis on Polyurethane Downstream Industries
1. Refrigerator Industry
Refrigerators mainly use polyurethane closed-cell foam as insulation material. Thailand, as a key refrigerator exporter in Southeast Asia, this round of anti-dumping investigation has almost blocked its export channel to the U.S., leading to a significant reduction in local demand for polyurethane foam materials. Other countries like Vietnam and Malaysia face the same general tariff barriers, which will hit regional PU insulation material producers in the short term.
2. Soft Furniture Industry
Sofa, mattresses, and other furniture widely use polyurethane flexible foam. Vietnam, one of the largest furniture suppliers to the U.S., the 46% tariff will significantly reduce exports. U.S. furniture importers may shift to other countries to control costs, indirectly weakening the Southeast Asian polyurethane foam market.
3. Footwear Industry
Polyurethane microcellular foam is commonly used in shoe soles and insoles. Southeast Asia is a major global footwear manufacturing hub, with Vietnam and Indonesia exporting footwear products to the U.S. worth over billions of dollars. High tariffs will force brands to restructure their supply chains, reducing the scale of polyurethane footwear material use.
IV. Summary and Outlook
The new round of U.S. tariff policies has impacted Southeast Asian export industries from multiple aspects, directly hitting the polyurethane downstream sectors of refrigerators, furniture, and footwear. In the short term, polyurethane demand in the region will tend to be weak, and raw material companies need to reassess capacity utilization and order sources. Southeast Asian countries should accelerate the process of market diversification, promote domestic demand growth, enhance industrial chain added value, and strengthen resilience and adaptability in the face of an uncertain global trade environment.