President Donald Trump has launched an investigation into imported furniture under the Section 232 national security statute, signaling the potential imposition of additional tariffs. The stated objective is to safeguard U.S. national security while revitalizing domestic furniture manufacturing, which has sharply declined over recent decades. Trump highlighted that new tariffs could incentivize production in key states such as North Carolina, South Carolina, and Michigan. The investigation is expected to conclude within 50 days.
In 2024, the U.S. imported $25.5 billion worth of furniture, a 7% increase from 2023, with nearly 60% of imports coming from Vietnam and China. Existing tariffs have already contributed to rising consumer prices, with home furnishings costs increasing by 0.7% in July 2025. Following the announcement, shares of furniture retailer RH fell 7.5% in after-hours trading, reflecting investor concerns over potential supply chain disruptions.
The American Home Furnishings Alliance (AHFA), representing U.S. manufacturers and importers, has opposed the investigation. Earlier in 2025, the AHFA led a coalition against similar tariffs on lumber and wood imports, arguing that such measures have little connection to national security and are unlikely to restore U.S. furniture production to previous levels. Instead, tariffs could disrupt supply chains relied upon by domestic manufacturers.
Impact on Asia’s TDI supply chain
Vietnam and China, as the two largest exporters of furniture to the U.S., are expected to be the most affected by potential new tariffs. For Vietnam, the furniture sector has experienced rapid growth, supported by low labor costs, advanced production capacity, and favorable trade agreements such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). Higher tariffs could compress profit margins for exporters, prompting manufacturers to accelerate production in the short term to fulfill pending orders, which would temporarily boost demand for raw materials like TDI-based flexible foam used in upholstered furniture and mattresses. Vietnam also relies heavily on China for critical raw materials, meaning any disruption in trade flows or tariffs could complicate production planning.
China, as the largest U.S. furniture supplier, may see its competitiveness decline, leading manufacturers to increase output before tariffs take effect or explore alternative markets in Europe, the Middle East, or Southeast Asia. Regionally, the investigation introduces uncertainty across the Asia-Pacific furniture manufacturing ecosystem, with potential stockpiling of both finished goods and raw materials driving short-term TDI demand.
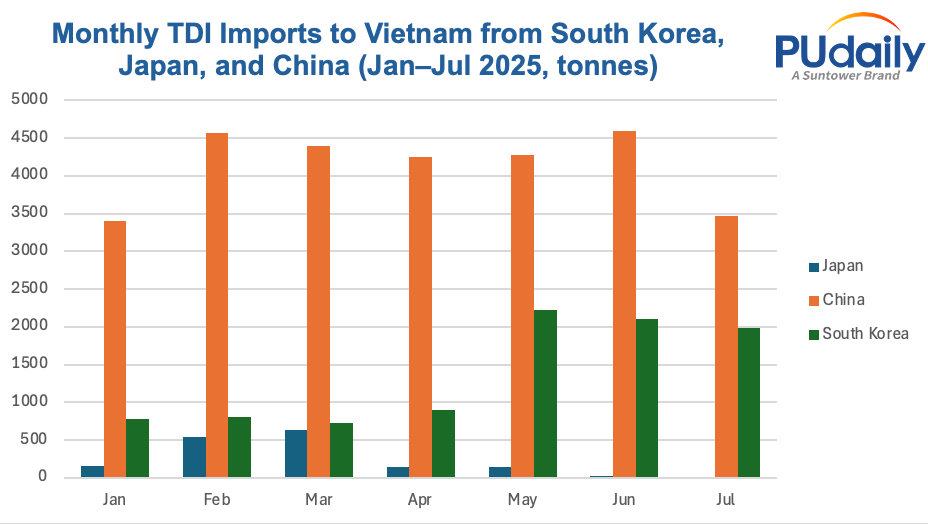
Downstream TDI users in Vietnam’s furniture sector are expected to boost short-term TDI purchases to scale up production for the U.S. market. Flexible foam, a key TDI derivative, plays an essential role in furniture manufacturing. While both Vietnam and China dominate furniture exports to the U.S., Vietnam also remains heavily dependent on China for TDI supply. From January to July 2025, China was Vietnam’s largest TDI supplier, exporting 28,949 tonnes, followed by South Korea with 9,511 tonnes. Japan’s contribution was significantly lower, with 1,638 tonnes exported as of June 2025.
Conclusion
In the short term, the investigation by the United States government on the import furnitures is expected to boost TDI demand among Vietnamese and Chinese furniture manufacturers. Over the longer term however, the global polyurethane value chain could face further disruption, depending on the investigation’s outcome and any resulting tariffs. Overall, the probe introduces immediate production incentives while generating long-term strategic uncertainties for both Vietnam and China, with significant implications for the wider downstream TDI and polyurethane supply chains.
Given these unpredictable dynamics, access to accurate, real-time market intelligence has become essential. PUdaily’s Pricing Intelligence Service and dedicated Asia-Pacific TDI reports help industry participants anticipate shifts, benchmark prices, and make better-informed procurement and sales decisions amid the uncertainty.